Submodules¶
Large projects can be split into smaller parts using submodules. A submodule contains the name, url and revision of another repository. To create a submodule in an existing git repository you need to add a link to another repository containing the files of the submodule.
Manage submodules¶
The current state of the submodules can be viewed with the Manage submodules function. All submodules are shown in
the list on the left.
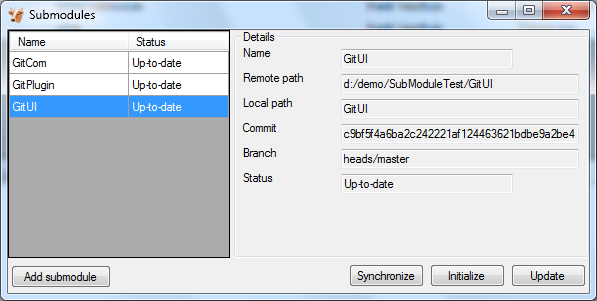
| Add submodule | Add a new submodule to the repository |
| Synchronize | Synchronizes the remote URL configuration setting to the value specified in .gitmodules for the selected
submodule. |
| Initialize | Initialize the selected submodules, i.e. register each submodule name and url found in .gitmodules into
.git/config. The submodule will also be updated. |
| Update | Update the registered submodules, i.e. clone missing submodules and checkout the commit specified in the index of the containing repository. |
Add submodule¶
To add a new submodule choose Add submodule in the Manage submodules dialog.
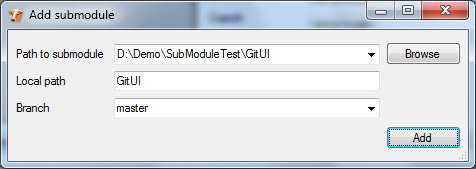
| Path to submodule | Path to the remote repository to use as submodule. |
| Local path | Local path to this submodule, relative to the root of the current repository. |
| Branch | Branch to track. |
Remove submodule¶
It is currently not possible to remove a submodule using the Git Extensions user interface. To remove a submodule you need to manually:
- Delete the relevant line from the
.gitmodulesfile. - Delete the relevant section from
.git/config. - Run
git rm --cached path_to_submodule(no trailing slash). - Commit and delete the now untracked submodule files.
